java-hashcode의 이해
hashCode()
- 객체의 주소값을 변환 생성한
고유한 정수값 - …인데 100프로 고유한 값만 내는 건 아님.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
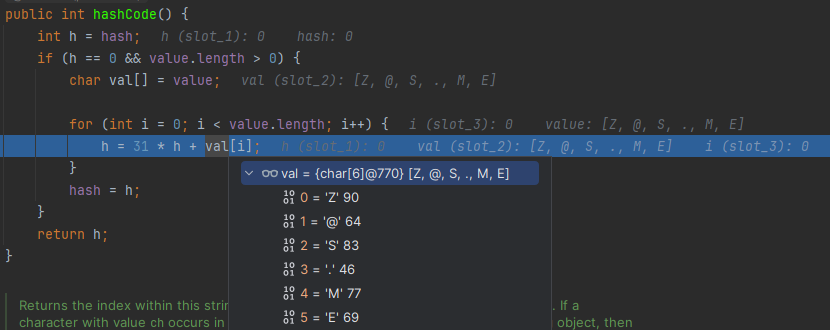
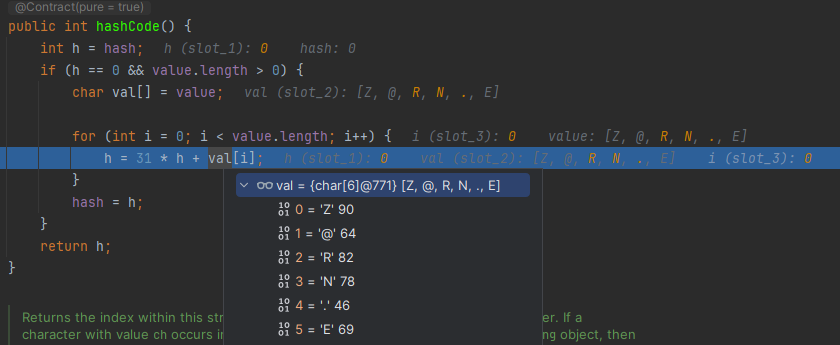
@Test public void hashCodeTest() { String a = "Z@S.ME"; String b = "Z@RN.E"; System.out.println(a.hashCode()); // -1656719047 System.out.println(b.hashCode()); // -1656719047 }
- 다른 String값이지만 hashCode() 결과값이 같다.
- 왜? 문자열을 ascii 값으로 가져와서 정수 연산을 하기 때문
그래서?
- 객체 비교의 기준을 세워야 할 때
- 객체 멤버(들)의
값을 기준으로 같다 틀리다의 기준을 세울 수 있음.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.HashMap;
import static org.hamcrest.core.Is.is;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertThat;
public class HashCodeTest {
@Test
public void hashCodeTest() {
String a = "Z@S.ME";
String b = "Z@RN.E";
assertThat(a.hashCode() == b.hashCode(), is(true));
}
@Test
public void hashCodeOverride() {
String abc = "abc";
String abc2 = new String("abc");
assertThat(abc.equals(abc2), is(true));
Person a = new Person("abc");
Person b = new Person("abc");
assertThat(a.equals(b), is(true)); // (동등성 비교) 이름이 같을때 같게 주고 싶다면? equals 오버라이드
assertThat(a.hashCode(), is(b.hashCode())); // (동일성 비교) string 값이 같을 때 두 인스턴스가 동일하다고 기준 잡고 싶다면? hashCode 오버라이드
}
@Test
public void hashMapPut(){
HashMap<Person, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Person p1 = new Person("abc");
Person p2 = new Person("abc");
map.put(p1, 10);
map.put(p2, 20);
System.out.println(map.size()); // 1
System.out.println(map.get(p1)); // 20, p2와 키 중복이므로 덮어씀.
}
}
class Person {
String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
Person anotherPerson = (Person) obj;
return this.name.equals(anotherPerson.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int hashCode = 0;
// String의 문자열 같으면 hashCode도 같음을 이용하여 객체 비교간 '같음'의 기준을 정의함.
return 31 * hashCode + (this.name.isEmpty() ? 0 : name.hashCode());
}
}
hashCode() 까지 같게 만들어서 어디에 쓸 수 있나?
- 위 테스트 메소드
hashMapPut()참고.
결론
- 객체간의 비교 기준은
equals()와hashCode()두가지 기준으로 비교 가능하다. - 기준은 요건에 따라 정하기 나름임.
- 예)
Person.nameString 멤버가 같다면 다 같은Person으로 볼 수 있다 같은 요건.
- 예)
HashMap 콜렉션에put()할땐equals()&&hashCode()모두 같아야 같은 키로 보고 중복제거한다.- equals는 비교할려는 두 객체의 내용이 동일한지? (동등성)
- ..그래서 동등한 기준으로 비즈니스 로직 처리를 어떻게 수행할건지?
- hashcode는 비교할려는 두 객체가 같은 객체인지? (동일성)
- ..그래서 동일한 기준으로 객체들의 모음(Collection) 중복처리 등을 어떻게 수행할건지?
참고
https://brunch.co.kr/@mystoryg/133
java.lang.String
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.